back
Social Disparities and Vulnerability to Resource Crises
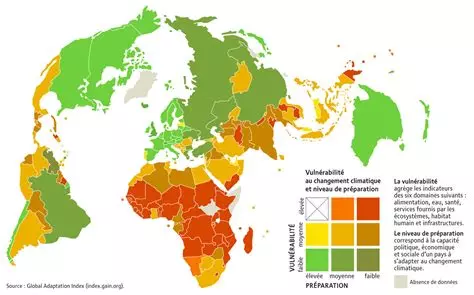
Social disparities refer to the inequalities between individuals or groups within a society, concerning areas such as income, education, health, employment, and housing. These inequalities can be linked to factors such as social class, gender, ethnic origin, or economic status. They create differences in opportunities and can lead to the exclusion or marginalization of certain populations.
Social disparities amplify the effects of the resource crisis. The poorest populations often have less access to essential resources such as water, food, and energy.
Developing countries, particularly in Africa and Asia, are especially vulnerable. They suffer from extreme climatic conditions, ineffective resource management, and limited infrastructure, which exacerbates their precariousness.
Wealthy countries, although better equipped to manage crises, are not immune. Internal inequalities can also exacerbate tensions around available resources.

